Perinatal care is the medical care that a pregnant woman receives around the time of delivery. Quality perinatal care is essential for a safe delivery and the health of both the baby and mother. Babies have a better chance of being healthy if they have the appropriate amount of time to develop before being delivered.
Guidelines from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend that babies should not be delivered until 39 completed weeks of gestation (or time in the uterus). This gives the baby’s brain, lungs and other vital organs the time to develop and lowers the risks of vision, hearing, respiratory (breathing) and other health problems related to premature fetal development. Hospitals should reduce the number of early elective deliveries that are not medically necessary, but done for the convenience of the patient or physician.
The graph below shows Lexington Medical Center’s performance in following best practices (evidence-based processes of care) when providing perinatal care for pregnant women. A column with N/A indicates one of the following: we did not have enough eligible patients to report on that measure; CMS held the data for one or more quarters; results were unavailable for the reporting period; no cases met the criteria for the measure; or results could not be calculated for the reporting period.
The reports on our site include information from Hospital Compare as well as our most current data available.
Guidelines from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend that babies should not be delivered until 39 completed weeks of gestation (or time in the uterus). This gives the baby’s brain, lungs and other vital organs the time to develop and lowers the risks of vision, hearing, respiratory (breathing) and other health problems related to premature fetal development. Hospitals should reduce the number of early elective deliveries that are not medically necessary, but done for the convenience of the patient or physician.
The graph below shows Lexington Medical Center’s performance in following best practices (evidence-based processes of care) when providing perinatal care for pregnant women. A column with N/A indicates one of the following: we did not have enough eligible patients to report on that measure; CMS held the data for one or more quarters; results were unavailable for the reporting period; no cases met the criteria for the measure; or results could not be calculated for the reporting period.
The reports on our site include information from Hospital Compare as well as our most current data available.
Early Elective Delivery
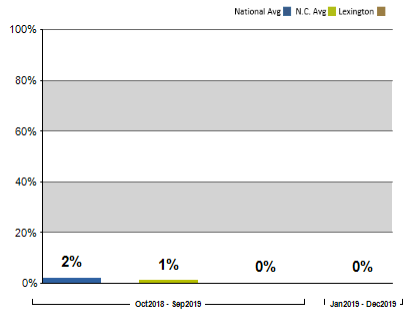
Babies who are born full term, or at 39 weeks completed gestation (time in the uterus), have lower risks of health problems related to premature fetal development. Although some early deliveries are unavoidable due to medical reasons or when labor occurs spontaneously, elective deliveries (by inducing labor or delivering a baby early by a cesarean operation) are not recommended. Elective deliveries are most often done for the convenience of the physician or patient. This chart shows the percent of patients who had elective vaginal or cesarean deliveries one to three weeks early when it was not medically necessary.
